Bismarckia nobilis
| Bismarckia (biz-mark'-ee-ah) nobilis (noh-BILL-ihs) | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
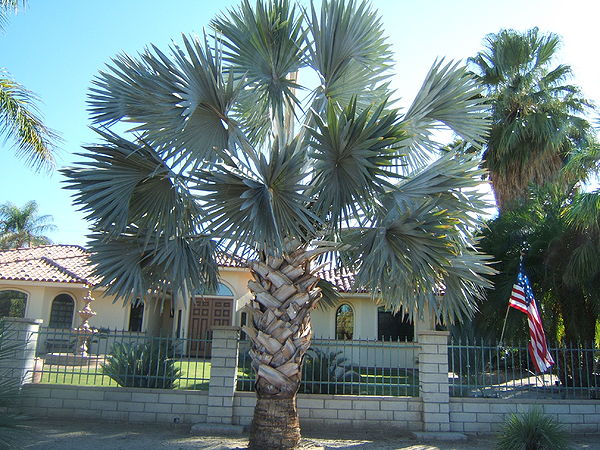
 Montgomery Botanical Centre, Florida, Photo by Dr. William J. Baker, Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew/Palmweb. | ||||||||
| Scientific Classification | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Synonyms | ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Native Continent | ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Morphology | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Culture | ||||||||
| ||||||||
| Survivability index | ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
| Common names | ||||||||
|
| ||||||||
Contents
Habitat and distribution
Bismarckia nobilis is endemic to western and northern Madagascar where they grow in open grassland, plateaux, plains, in all terrains; very common, in large numbers as the only tree on regularly burnt palm
Description
Bismarckia is a monotypic palm genus named for the first chancellor of the German Empire, Prince Otto von Bismarck and the epithet for its only species, Bismarckia nobilis, comes from Latin for 'noble'.
Or, to put it another way, there's only one species, but what a species!
B. nobilis grows from solitary trunks, gray to tan in color, which show ringed indentations from old leaf bases. Trunks are 30 to 45 cm in diameter, slightly bulging at the base, and free of leaf bases in all but its youngest parts. In their natural habitat they can reach above 25 meters in height but usually get no taller than 12 m in cultivation. The nearly rounded leaves are enormous in maturity, over 3 m wide, and are deeply-divided into 20 or more stiff segments. The leaves are costapalmate, producing a wedge-shaped hastula where the blade and petiole meet. Petioles are 2-3 m, slightly armed, and are covered in a white, waxy material as well as cinnamon-colored scales; the nearly-spherical leaf crown is 7.5 m wide and 6 m tall. Most cultivated Bismarckias feature silver-blue foliage although a green leaf variety exists (which is less hardy to cold). These palms are dioecious and produce pendent inflorescences of small brown flowers which, in female plants, mature to a brown ovoid drupe, each containing a single seed.
| Detailed Scientific Description |
|---|
|
Solitary palm 2-20 m tall (the 30-50 m mentioned in Stein, 1886 is surely an exaggeration). TRUNK smooth, grey-brown, cylindrical, very straight, 20-40 cm in diam., to 80 cm at very base, often marked distally with spiral twists, either clockwise or counterclockwise; internodes about 1.5 cm; pith abundant, white. LEAVES 13-30 in the crown, porrect to slightly arching, marcescent in immature individuals, neatly abscising under their own weight in mature trunked individuals; sheath about 80 cm long, pale brown with a white-waxy covering and with scattered laciniate scales, at the interface with the petiole with 2 auricles in the shape of a 90° bend in the sheath edge; petiole 70-250 cm, proximally 12 x 3.5 cm in diam., distally 3.5-5.5 x 1.3-2.5 cm in diam., abaxially convex, adaxially almost flat to channelled, the surfaces greyish white, densely cov ered in white wax and patches of reddish, fringed caducous scales, with sharp edges or with minute, 1 mm long teeth, grey-waxy; blade about 1.5 m diameter at greatest width, 50 cm at shortest, blade held mostly flat, grey, yellowish by the hastula, interfold filaments conspicuous, costa 43 cm, segments 50-77, inserted on one side 2-11 cm lower than on the other, the outermost undivided for about 25-50%, 42-80 x 1.7-3 cm, the innermost undivided for about 80%, 79-87 x 4.1-6 cm, slightly waxy abaxially with pale grey-brown ramenta on the midrib, transverse veinlets very faint or not visible. STAMINATE INFLORESCENCES branched to 2 orders; bracts 5-6, acute; first order branches 30-35 x 3.5 x 0.5 cm; rachillae digitate, in groups of 1-9 at the end of the branches, crimson, 15-25 cm long, 0.8-1 cm across; floral bracteoles thick, short, wide. STAMINATE FLOWERS with the sepals ovate, acute, about 3.5 mm long; petals obtuse, about 7 mm long, connate in the lower half; stamens 7 mm, with long thin filaments; ovary rudiment about 3.5 mm high. PISTILLATE INFLORESCENCES interfoliar, (x: sight records) erect, about 120 cm, branched to 2 orders; peduncle about 30 cm, proximally about 3.2 x 1.5 cm; prophyll about 28 cm; peduncular bracts inserted at about 7 cm, about 41 cm long (closed for about 22 cm), inserted at about 12 cm and about 50 cm long (closed for about 29 cm); rachis about 66 cm; first order branches 36-44 cm long, proximally about 16 x 8 mm across, distally about 13 x 4 mm across, straw-yellow, glabrous except for the most distal part bearing some scattered scales, with 2-5 digitately arranged rachillae; rachillar bracts 27-53 cm, cylindrical, open only distally, proximally glabrous, distally with dense or scattered scales; rachillae 15-23 cm long, 1-1.5 cm across; floral bracteoles thick, short, 2-3 mm high, 8-16 mm wide. Pistillate flowers stalked, the pedicel hairy, elongating after anthesis; sepals about 3 x 3.5 mm, similar to the petals, but more acute; ovary oblong, stigmas quite early in development lateral-basal. FRUIT dark brown, ovoid, obtuse, 40-48 x 30-35 mm, flanked at base by 2 aborted carpels, or occasionally bi- or tri-lobed, with crustaceous pericarp, spongy mesocarp and hard endocarp. SEED 35-38 x 22-24 mm; endosperm homogeneous but penetrated by ridges on the inside of the endocarp. (J. Dransfield and H. Beentje. 1995)/Palmweb. Editing by edric. |
Culture
"To dig a bismarckia, is nearly to kill it." (Rafael)
Blue/silver form in Mediterranean climate: This is a great palm for such a climate, but it never looks quite as amazing/majestic as it does in a more tropical climate. It is highly tolerant of intense, inland heat, growing fastest where it is the hottest. However, it also grows well along the coast of such a climate- but significantly more slowly and with less intense coloration. It is best to grow this palm in a well draining soil, but palms grown in dense clay soils seems to do pretty well. Keeping the soil moist sure seems to keep this palm happier.
Full sun is the best location for this palm. Unfortunately full sun often means the most intense cold exposure in the winter. It is cold tolerant down to the high 20s/-3.3C as a seedling, often being defoliated at temps below 27F/-2.77C (but usually recovers if the bud is treated well). However, as this plant matures its cold tolerance seems to improve dramatically, with some palms surviving temps down near 22F/-5.55C with only moderate leaf damage. Over winter this is one of those palms that tends to go 'into a coma' often not showing the least bit of growth for 4-6 months at a time. However, once it warms up, it is not unusual to see some palms produce up to 1-2 leaves a month (the larger the faster it grows) which is very fast for a Mediterranean climate palm.
Green form in a Mediterranean climate: Though this form is much faster growing than the blue form in tropical climates, the opposite tends to be true in a Mediterranean climate. In fact, in most such climates, this is known as a very marginal palm, often unable to tolerate much freezing weather at all, and sulking dramatically in prolonged cool seasons. It's culture is so different from the blue-silver forms, that it seems like a totally different species. It is very rare to see this color form growing in a Mediterranean climate, and even rarer to see one in such a climate and healthy looking. This palm always seems to battling some bud-related damage problems. It is not unusual for exceptional palms that seem to be growing well to just up and die with no apparent reason.

Comments and Curiosities
This genus is dioecious, separate male, and female trees.
This must be the most common palm in Madagascar. It is a handsome palm, which does well in the drier tropics and subtropics and is planted in many countries. The genus is named for the German chancellor, Otto von Bismarck (1815-1898), one of the few cases where botanists have named a species after a politician. When Madagascar was colonized by the French, they included the species in Medemia, thus getting rid of the name Bismarckia, but most botanists (including the present authors) regard the genera as distinct, and therefore Bismarckia is the correct name for the Madagascar palm. (J. Dransfield and H. Beentje. 1995)/Palmweb.
Conservation: Not threatened. Widespread and very common.
Uses: Trunk emptied and flattened for use as planks or in partition walling; leaves used for roofing and basketry; pith serves as a slightly bitter sago. Outside Madagascar a prized ornamental for the drier (sub-) tropics.
Has almost become common, in Southern California. They have invaded Big Box stores, almost like the "Gremlins" from the movie. The silver form makes newbies to palms scream. Especially against a dark green background.
- IMAGE GALLERY
| MORE PHOTOS |
|---|
|
External Links
- Glossary of Palm Terms
- MODERN BOTANICAL LATIN
- "Just To Be Clear"
- http://itp.lucidcentral.org/id/palms/palm-id/Bismarckia_nobilis.htm
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=M8JrqhG61A8
- http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=YpKiKt-FHis&feature=related
- http://www.cites.org/common/com/pc/20/inf%20docs/F20-11i-A6.pdf
References
Phonetic spelling of Latin names by edric.
Special thanks to Geoff Stein, (Palmbob) for his hundreds of photos.
Special thanks to Palmweb.org, Dr. John Dransfield, Dr. Bill Baker & team, for their volumes of information and photos.
Glossary of Palm Terms; Based on the glossary in Dransfield, J., N.W. Uhl, C.B. Asmussen-Lange, W.J. Baker, M.M. Harley & C.E. Lewis. 2008. Genera Palmarum - Evolution and Classification of the Palms. Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew. All images copyright of the artists and photographers (see images for credits).
Dransfield, J. , Uhl, N. , Asmussen, C. , Baker, W.J. , Harley, M. & Lewis, C. 2008. Genera Palmarum. The evolution and classification of palms. Kew Publishing, Royal Botanic Gardens Kew.
Many Special Thanks to Ed Vaile for his long hours of tireless editing and numerous contributions.